New battery security rules regarding thermal runaway have prompted an evolution in pack design
In 2020, the Chinese language authorities issued GB 38031, a brand new nationwide security normal for electrical automobiles. It set a brand new requirement for car security through which passengers should obtain at the very least a five-minute warning to exit the car if a battery thermal runaway occasion is detected. Earlier this 12 months, a revised normal was issued, which tightened these security necessities significantly. Whereas the five-minute egress rule nonetheless stands, the usual is now extra prescriptive round failure modes, testing, documentation and efficiency.
Thermal boundaries are one of many key applied sciences required to satisfy this normal. In pouch- or prismatic designs, thermal boundaries are usually positioned between every cell to function a firewall. If one cell goes into thermal runaway, thermal boundaries reduce off the cell-to-cell conduction that’s the first pathway for thermal vitality to journey. Thermal boundaries can not cease the spark, however that may delay or stop it from lighting the fuse. Whereas GB 38031-2025 doesn’t explicitly require thermal boundaries, it’s now a lot tougher to adjust to the usual with out them.
On the identical time, EV batteries are getting larger. Larger vitality densities, tighter packaging, and shorter design cycles imply there’s much less room — actually and figuratively — for error. To forestall a single-cell thermal runaway from propagating into adjoining cells, designers have to pack as a lot thermal resistance as doable into the tiny gaps between cells. However how a lot is important?
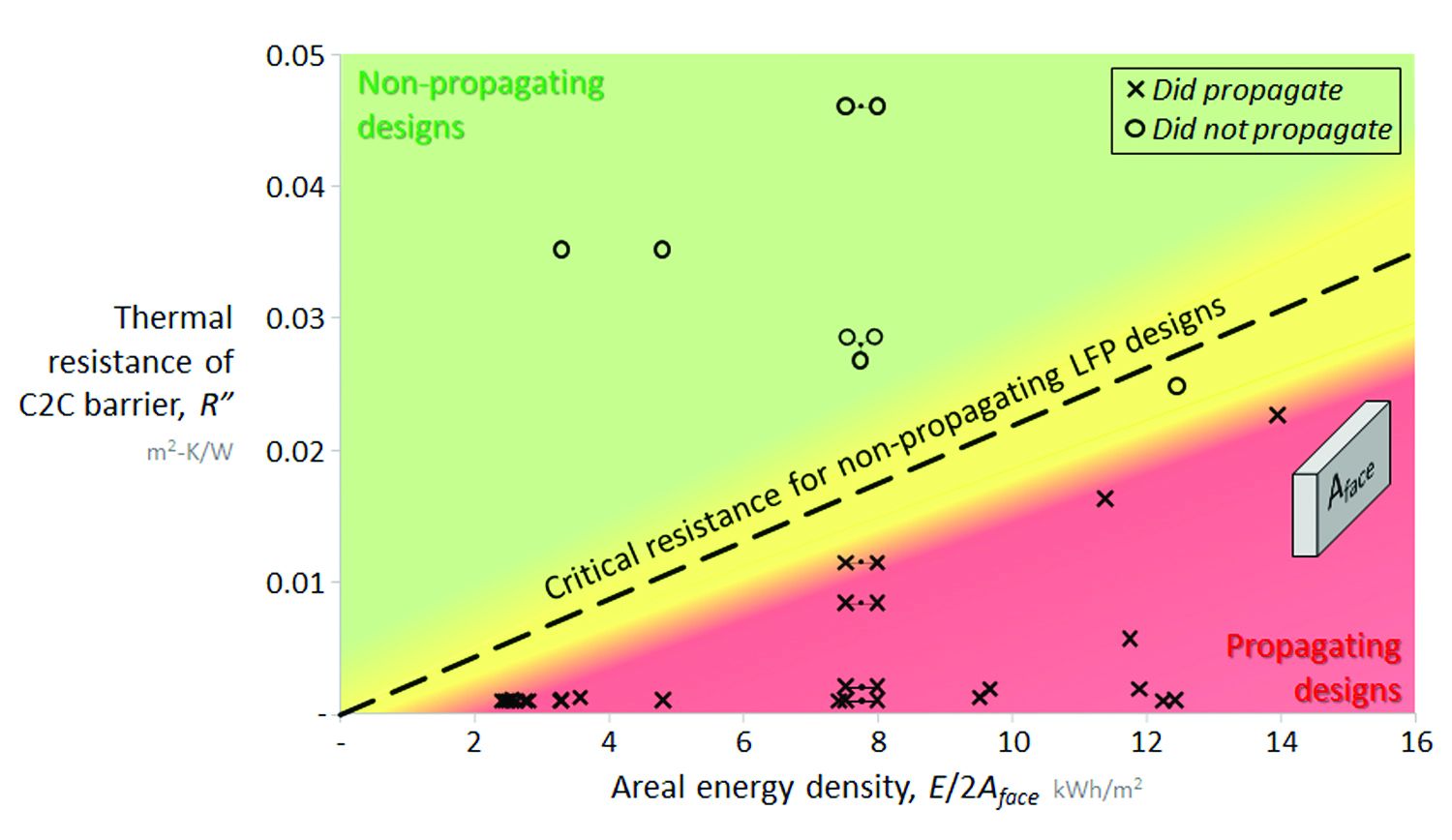 It seems there’s a easy proportionality between the vitality content material of the cells, the cell-face space, and the important thermal resistance of the thermal barrier. That proportionality will be discovered by conducting a number of thermal runaway assessments through which thermal boundaries of various thickness are trapped between two cells in an open-air setting. By triggering one cell into thermal runaway and monitoring whether or not the opposite cell follows it, two populations will be recognized: propagating and non-propagating designs. These populations are separated by a boundary denoting the important thermal resistance beneath which thermal propagation will happen.
It seems there’s a easy proportionality between the vitality content material of the cells, the cell-face space, and the important thermal resistance of the thermal barrier. That proportionality will be discovered by conducting a number of thermal runaway assessments through which thermal boundaries of various thickness are trapped between two cells in an open-air setting. By triggering one cell into thermal runaway and monitoring whether or not the opposite cell follows it, two populations will be recognized: propagating and non-propagating designs. These populations are separated by a boundary denoting the important thermal resistance beneath which thermal propagation will happen.
This evaluation reveals that thicker, extra energetic cells require further thermal resistance to forestall propagation by cell-to-cell warmth switch. When the identical kind of testing is carried out on NMC cells, an identical linear boundary exists however with a taller slope. On account of their decrease trigger- and better peak-temperatures throughout runaway, NMC designs can require 50-60% extra insulation for a pack of the identical vitality capability.
Aspen Aerogels’ engineers have an in-depth understanding of the complicated mechanisms of thermal runaway. They design PyroThin cell-to-cell boundaries with a system-level strategy to not solely deal with thermal propagation but in addition maintain cell well being and efficiency all through the pack’s lifecycle.


